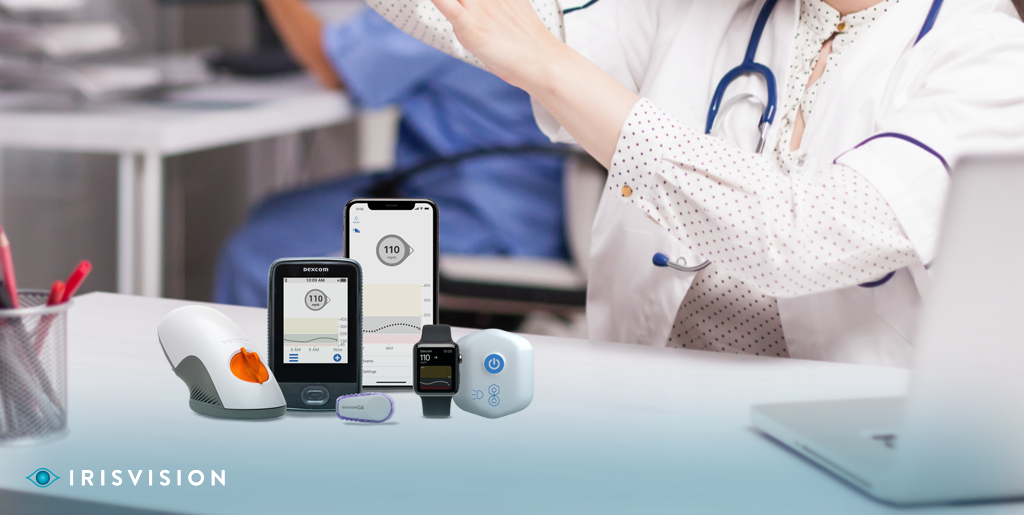
Wearable devices play a significant role in remote patient monitoring (RPM) by enabling continuous, real-time data collection and transmission. These devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and health monitoring patches, offer several benefits in remote patient monitoring:
- Vital Sign Monitoring: Wearable devices can collect and transmit various vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation levels. This allows healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ physiological parameters and detect any abnormal trends or fluctuations.
- Activity and Movement Tracking: Wearables can monitor patients’ daily activities, such as steps taken, calories burned, and sleep patterns. This data helps assess patients’ overall physical well-being, progress in rehabilitation programs, or adherence to activity recommendations.
- Medication Adherence: Some wearable devices are equipped with reminders and notifications to help patients adhere to their medication schedules. They can send alerts and track medication intake, improving patient compliance and reducing the risk of medication errors.
- Fall Detection and Safety: Wearables with built-in accelerometers and gyroscopes can detect sudden changes in body positions or movements indicative of falls. In such cases, alerts can be automatically sent to caregivers or emergency services, ensuring a timely response.
- Remote ECG Monitoring: Certain wearable devices can record and transmit electrocardiograms (ECGs) remotely. This is particularly useful for patients with cardiovascular conditions, as it allows for continuous monitoring of heart rhythms, detection of arrhythmias, and early intervention.
Role of wearable device and remote patient monitoring
- Remote Chronic Disease Management: Wearables enable continuous remote monitoring of chronic disease parameters, such as blood glucose levels for diabetes management. This data can be shared with healthcare providers in real-time, allowing for timely adjustments to medication, lifestyle interventions, or treatment plans.
- Patient Engagement and Self-Management: Wearables encourage patients to take an active role in their health management. By providing real-time feedback and personalized insights, wearables promote patient engagement, motivate behavior change, and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
- Proactive Intervention and Preventive Care: Through wearables, healthcare providers can receive real-time alerts and notifications when a patient’s vital signs or activity levels deviate from the expected range. This enables proactive interventions, preventing adverse events and promoting preventive care.
- Personalized Feedback and Coaching: Certain wearable devices offer personalized feedback and coaching based on the collected data. They can provide guidance on optimizing health behaviors, encouraging physical activity, managing stress, or improving sleep quality.
- Remote Patient-Provider Communication: Wearables facilitate remote communication between patients and healthcare providers. For example, patients can share their data or reports directly with their healthcare team via secure platforms, allowing for virtual consultations and continuous monitoring without the need for in-person visits.

